Squeezed-Entanglement Ephemeral Proof
A stateless, one-shot authentication proof built from continuous-variable quantum optics.
Approach
SEEP uses two-mode squeezed states (TMSS) and homodyne detection — mature, high-rate, room-temperature tools in quantum optics. Each authentication proof consumes shared quantum state, making replay impossible.
The protocol applies a local squeezing transform as a hardware signature, then tests entanglement via a variance-based witness adapted from Duan-Simon criteria.
Why it matters
Every key-based system has the same vulnerability: keys can be extracted. SEEP explores authentication where there's nothing to extract — security grounded in physical laws rather than computational hardness.
Classical and post-quantum cryptography both rely on mathematical assumptions. Physical laws don't break with better algorithms.
Simulation Results
Gaussian-state simulation using Strawberry Fields. Sweep over resource squeezing r ∈ [0.2, 1.5], channel transmissivity η ∈ [0.6, 1.0], and hardware squeezing r_h ∈ [0, 0.7]. Acceptance threshold: Var(Ô) < 0.95 shot-noise units.
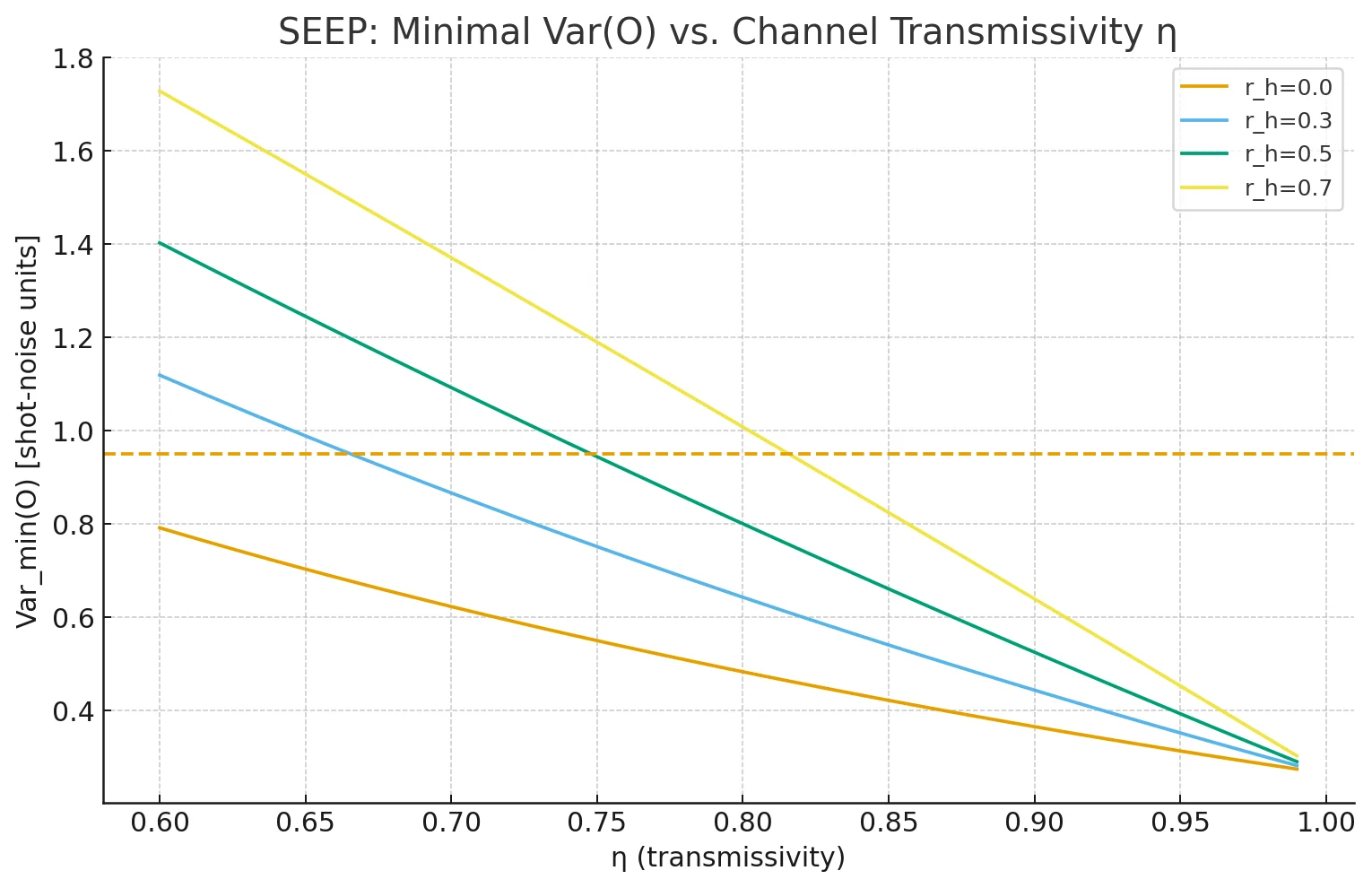
Variance vs. channel transmissivity for different hardware squeezing values. Dashed line = acceptance threshold.
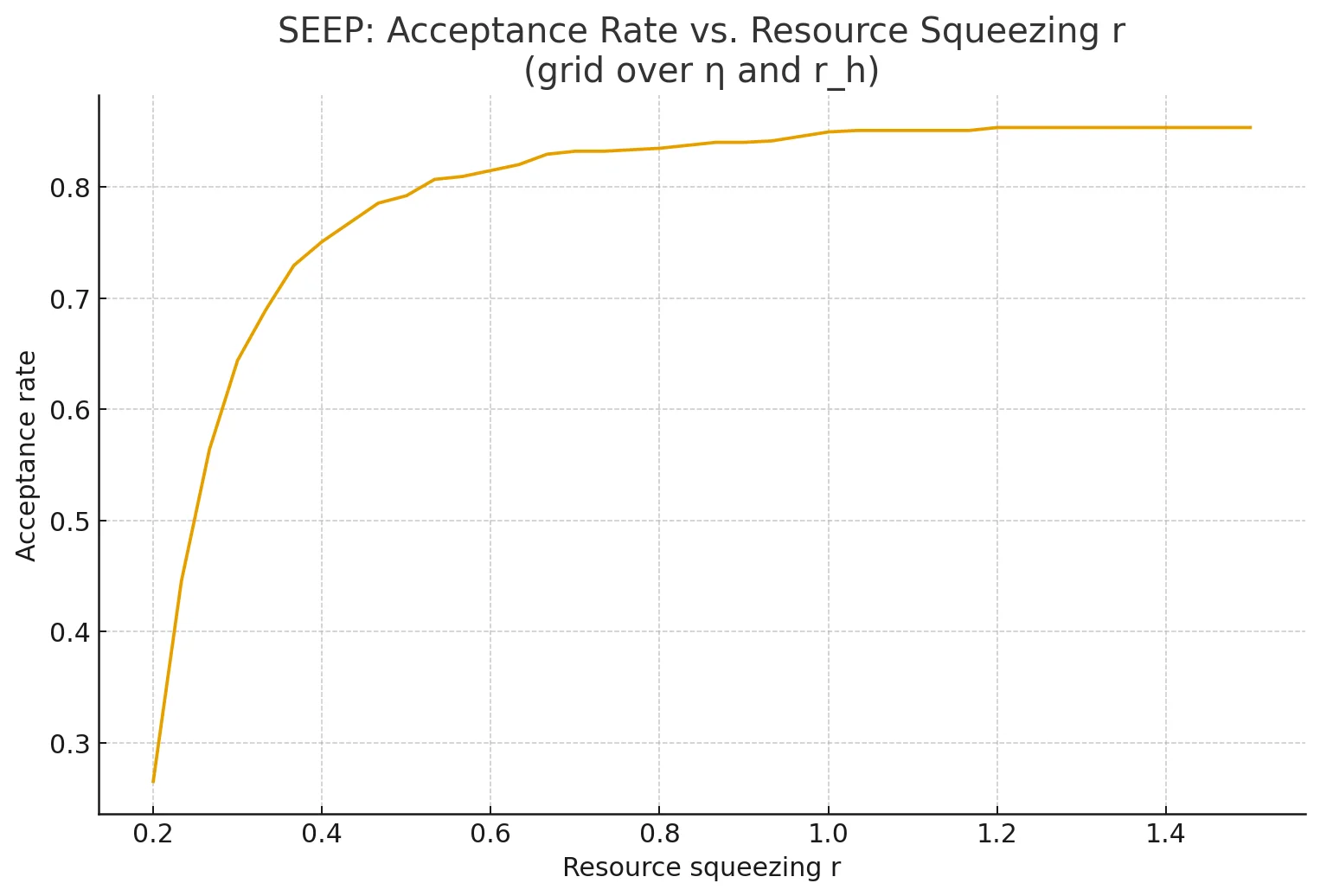
Acceptance rate vs. resource squeezing, averaged over parameter grid. Plateaus ~85% at higher squeezing.
Status
We're preparing a research note with methods, adversary model, and simulation results. Implementation details will be shared with research partners under NDA.
Last updated: December 2025
Partner with us
If you're working in CV-QKD, squeezed light generation, or physical unclonable functions and want to learn more, get in touch.
research@iampass.com →